Installing Fedora
In this article, we will:
- Install Fedora Server (This guide will be using Fedora 34)
- Select btrfs as the root filing system during partitioning for backups
Info
You can also use Fedora Workstation if you prefer having a graphical UI. However, this guide will work under the assumption that we are using the Server edition.
Why Fedora?
Fedora is a good choice for a docker environment for several reasons:
- Good blend of up to date software and stability
- Comes with the cockpit web management interface by default
- Allows for a btrfs root installation (important for backups later)
- Upstream of Red Hat distributions, which provides real business expertise.
Installation
- Image your Fedora server ISO to a removable media like a USB key. You can do this using dd in a Linux environment, or using Rufus in a Windows environment
Info
You can choose either DD or ISO mode for writing. I find DD to be more reliable.
- Once imaged, boot your machine from the USB to start the installation process. Once on the installation screen, we will set some settings:
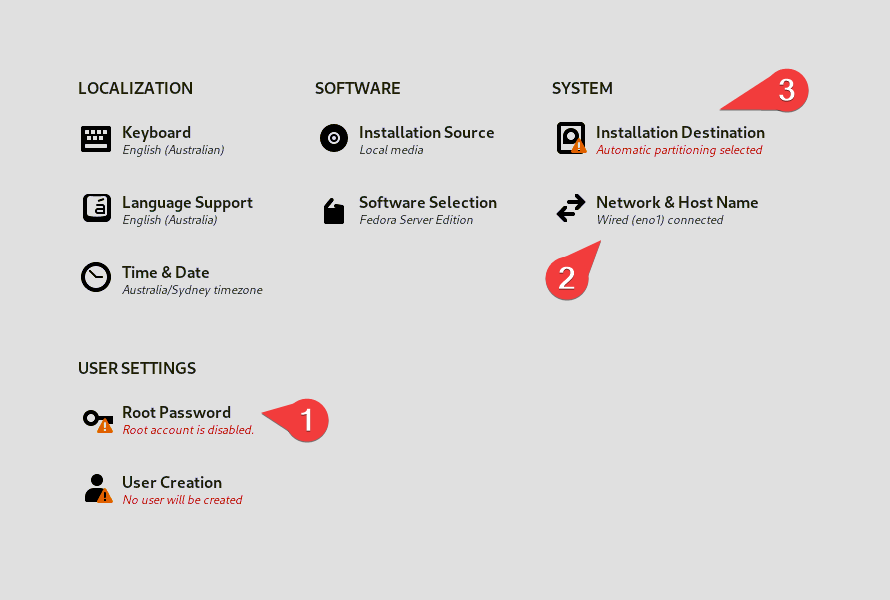
- On Root Password, set the root password:

Info
You do not have to (and should not) allow root SSH login with a password.
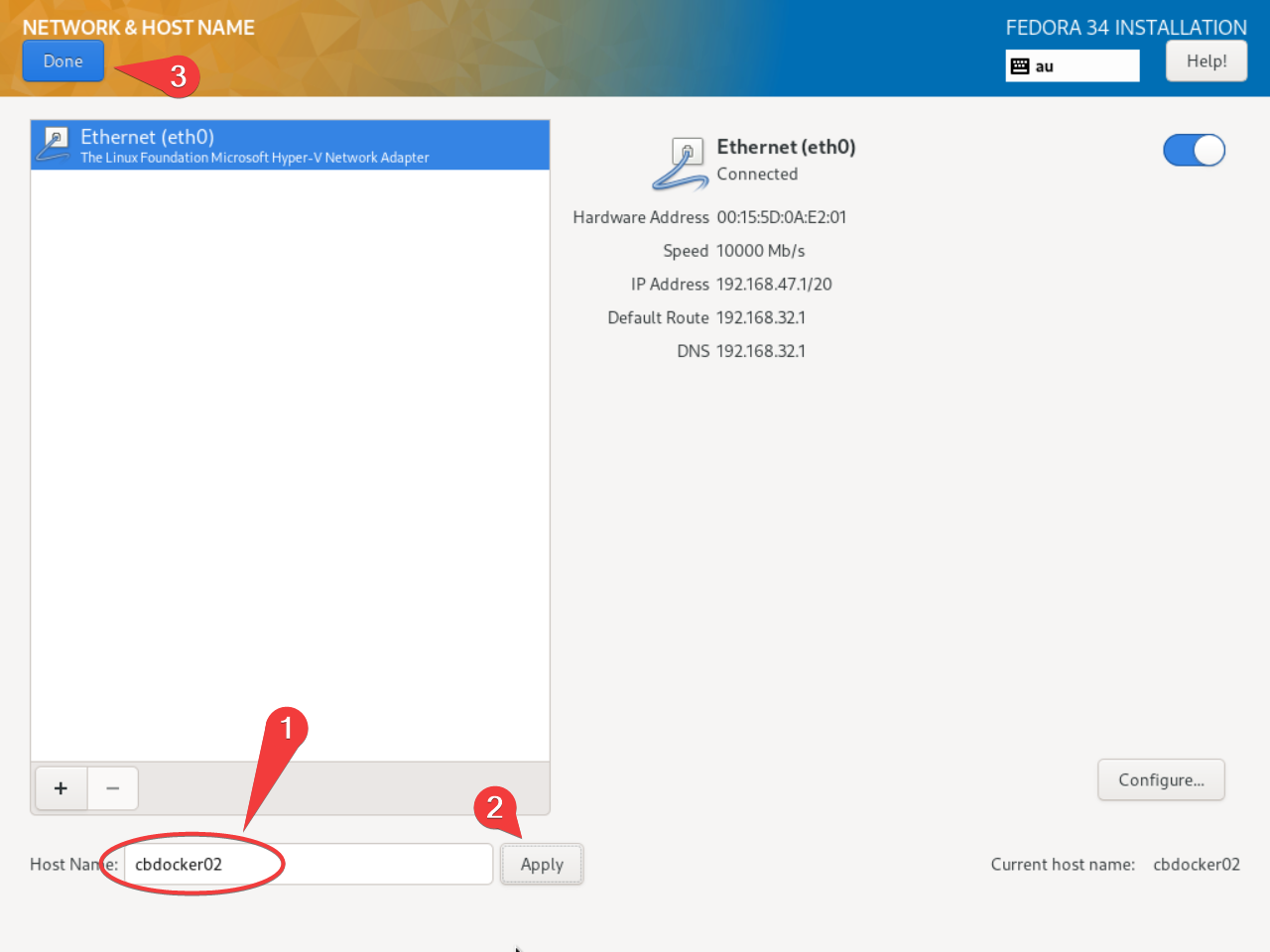
- Under Network, set the name of your machine, and optionally set a static IP
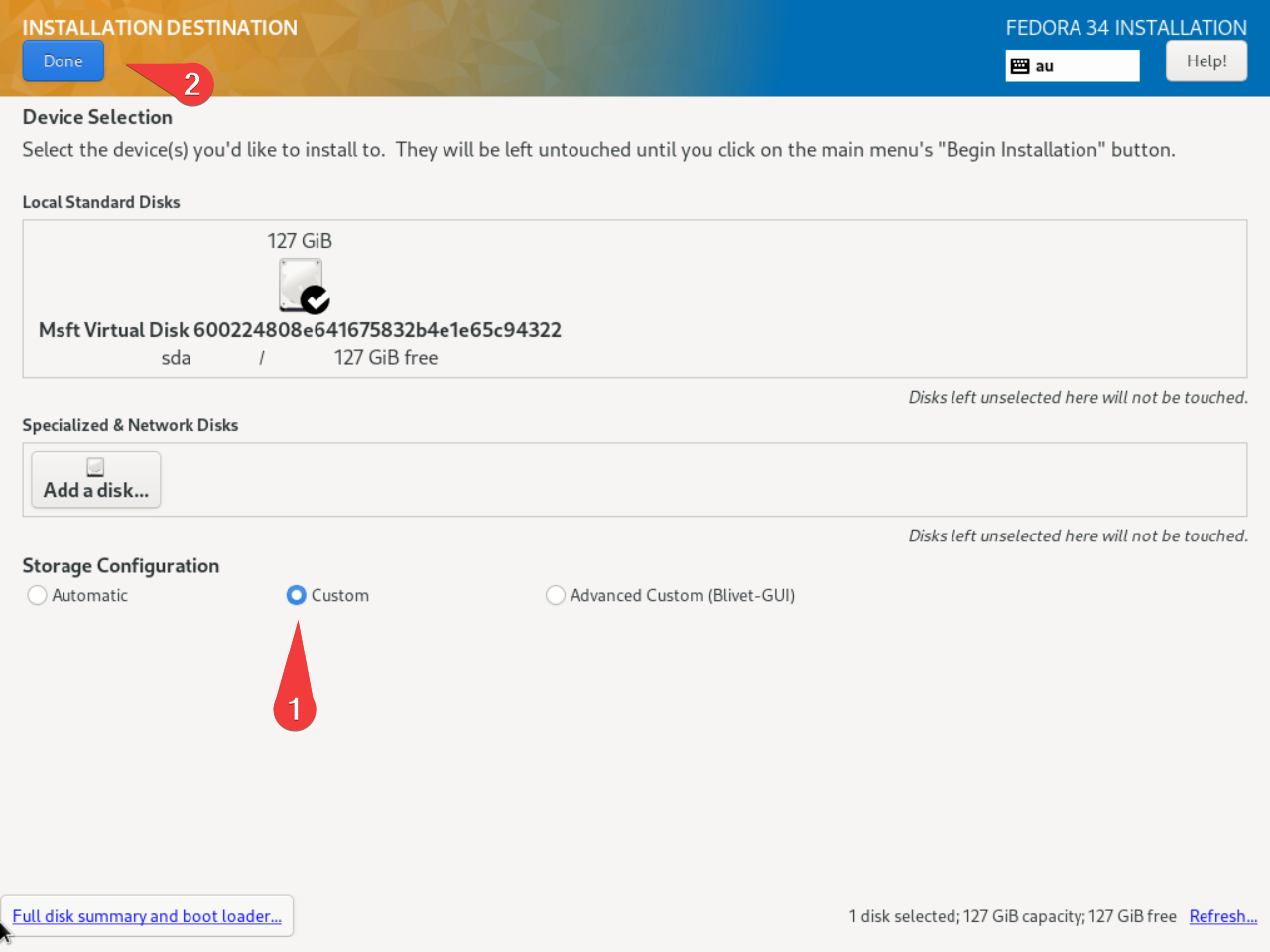
- Under Installation Destination, we will deviate a bit from the default storage. choose custom. Rather than using the default xfs partition system, we will default to a btrfs partition scheme.
Warning
You may have to delete existing partitions during this process if you want to overwrite any existing data. This deletes existing data!
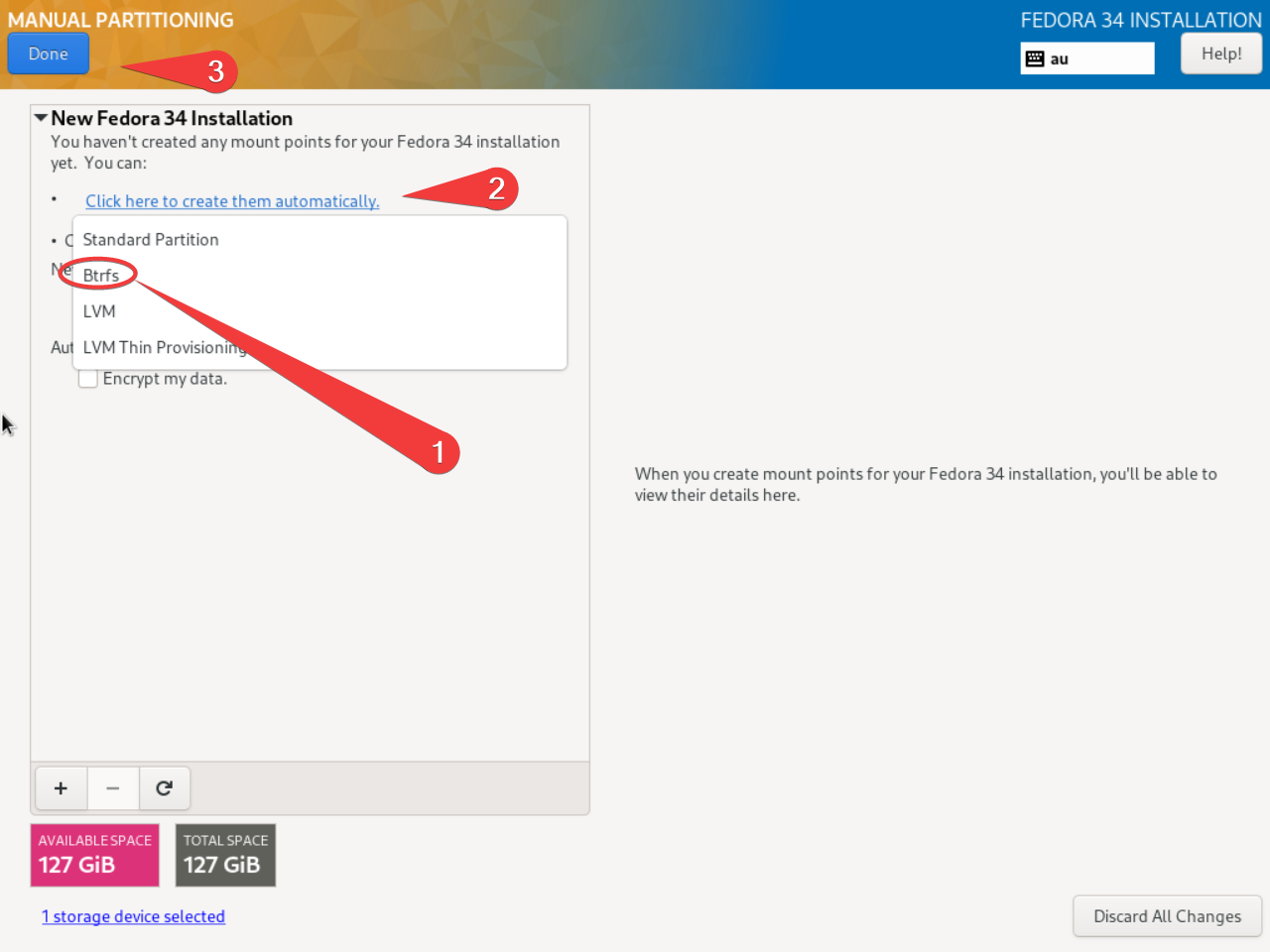
- After all that’s done, hit begin! Once finished and rebooted, you should be presented with a lovely blinking cursor: